
by Felicien | May 22, 2017 | Education
Google Analytics is a powerful suite of tools, but can be overwhelming at first: Here’s how to begin.
Google Analytics can be a godsend to young companies trying to grow online traffic to their website. It’s a free service provided by Google itself to track detailed website data and find out just what’s going on. For businesses without much experience in building and managing a website, Analytics can be a complex and daunting set of tools to dive into. Let us help by recommending several important steps when you are first setting up and finding out how Google Analytics works!
Keep an Unmodified Version of Your Site View
Google Analytics allows you to create properties based on your site and then specific “views” or reports of activity on your site. One of the first things that you should do when setting up is to create a base level reporting view of your site, just to see what it is. Keep that view separate – don’t add any filters or customization to, don’t change your websites and then redo it, just keep there, with the original data. This will be very useful when making long-term comparisons 6 months or a year out, when you can say, “This is where we started and here is where we are now.” This is particularly handy for ROI but also helps you create more accurate goals and not get lost in a mess of view reports without real purpose.
Use WebMaster Tools
Google Webmaster provides a variety of tools for you to research SEO trends and manage your website. You can link a WebMaster profile and an Analytics profile for your business, and this should certainly be another one of your first steps. Webmaster offers a number of useful tools for web designers, but it also provides valuable extra analysis. This is important since Google removed access to its primary keyword research tools on Analytics – Google generally tries to discourage “gaming the system” when it comes to keywords and thought that tool was providing a little too much actionable information. Webmaster provides a keyword research alternative that still allows you to find out useful SEO info for your content.
Prepare and Set “Goals” for Your Funnel
Goals are a specific tool in Google Analytics that allows you to research a very specific metric that you are concerned about our want to improve. As you set up your Analytics strategy, make sure that you create the right goals for your web pages and screens. Consider carefully beforehand just what you want to measure, from bounce rates and load times to single conversions and time spent on page. Every metric has its uses, but it’s smart to only pick a few viewer actions to measure in the beginning and make sure those actions connect with your goals.
Enable Site Search
Site Search is a handy capability that allows you to track search data within your website. This tool is particularly useful if you have an online product catalog or any type of complex website with different offerings and purchase opportunities. Site search will track exactly what terms visitors type in your site search bar to help them find something specific connected with your brand. These searches can tell you what people are interested in, and what they are having trouble finding via other means. It’s very handy!
Create a Schedule for Analysis
In general, Google Analytics is only useful if you use and make changes based on the information. Too many companies start Google Analytics but never progress or really use it for anything. So schedule a time – say, one afternoon a week – where you or your team sits down with Google Analytics, studies the latest results, and creates an updated plan based on what everyone has learned. Don’t let this tool go to waste.
Choose Some Extra Goals
When you feel confident enough, try a few extra, farther-reaching goals to track specific metrics that can provide very interesting information. That includes geo data for location-based results and more complex user paths to judge multiple events at the same time. You shouldn’t try to create goals for everything, but it’s good to sample different data sets from time to time, so start the habit early.
Do you have more questions about how to use Google Analytics and other research tools to improve your {city} website? Let {company} know how we can help! Contact us at {phone} or {email} to learn more.

by Felicien | May 22, 2017 | Education
The easy answer is money. Hackers infect your computer, lock up your data, and you pay to get it back. Easy to understand, right? The basics are. But if you’re like the average business computer user, you are now being newly exposed to terms like bitcoin, crypto mining and other terms that sound like they came directly from the latest Guardians of the Galaxy movie, not something we would deal with here on earth. Unfortunately, this is not the case.
Understanding all this can be confusing, and in a perfect world, something the average business owner shouldn’t have to worry about. The latest computer threats have changed all that. Basically, just as you already know, the computer tech world is just that, a world of its own, with its own language, structure, and of course, as you would expect, its own currency. Just like the currency we are familiar with, there are lots of types. Some examples include: Bitcoin, Namecoin, Dogecoin, Monero and many more. This currency, in most cases, is untraceable. Which means that, as you would expect, it is highly sought after, especially among those less reputable.
So why does it affect you? WannaCry last week exposed the world to the darker side of what a hacker can do—How your computer can literally be held for ransom. In the case of WannaCry, they wanted Bitcoin. During the clean-up of this attack, another virus was found named Adylkuzz. Unlike WannaCry, this virus doesn’t hold your computer ransom, in fact, you might never know it’s there because it’s basically invisible. Hackers created the virus to run processes on your computer that can earn the hacker cryptocurrency. How does this affect your business? It can slow down your entire network causing you time, and in some cases money.
Doesn’t sound like a big deal, right? It may not be, but it is to the hackers. In fact, the amount of cryptocurrency earned by hackers through Adylkuzz is way more than WannaCry.
Simply put, it’s no different than an employee stealing office supplies—A company may not notice, but it adds up after a while.
What can you do? The answer is simple, you’ve heard it time and time again—Make sure your software, especially Windows, is up-to-date. Like WannaCry, Adylkuzz found its way in because of outdated Windows software. It’s an easy fix.
Now more than ever, it’s important to have a trained professional involved in your computer support. The whole purpose of a good Information Technology Managed Service Provider is to ensure that you never have to worry about being hacked because your equipment or software was outdated, your security measures weren’t adequate, or because you just didn’t know what to look for. Call {phone} or send us an email to {email} today, to ensure your company’s IT is protected.
You have a choice. Learn a whole new language in addition to running your business, or hire a professional translator. {company} knows the language and the way the tech world works. Let us work for you.
by Felicien | May 22, 2017 | Education
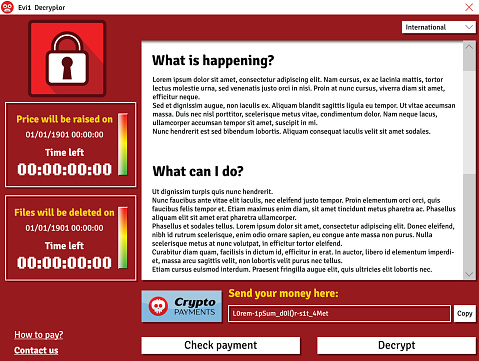
WannaCry may be beaten, but here’s why the ransomware can still be dangerous.
WannaCry is an infamous example of how dangerous ransomware can be in the modern world. Almost overnight, this cyber attack hit computers around the world and managed to infect 300,000 computers in more than 150 countries before going back to the benches for a break.
Ransomware is particularly dangerous because, unlike many types of malware, it has a particular purpose: It tries to extort money from victims by holding data hostage. In this case, WannaCry spread its way through unprotected Windows computers, locking away valuable files and changed desktop backgrounds into a set of commands to submit money to the hacker via bitcoins. Here’s how it played out.
How WannaCry was Born
WannaCry is an interesting version of ransomware because of the way that it spreads. Most ransomware starts with a relatively simple phishing email that encourages victims to click on the link and so download the malware. WannaCry, short for Wanna Decryptor, spreads itself through the Server Message Block protocol, which is used by Windows computers to share files. That makes it very easy for the malware to jump between different computers that are on the same Windows network (the actual mechanics of making that jump are still somewhat unclear). This makes the ransomware particularly dangerous for business and school computers that are regularly connected on large networks. It even managed to infect high-level government organizations in countries like the UK.
When inside a vulnerable computer, WannaCry chooses specific files types – files types generally known for their valuable data content – and creates an encrypted copy of them using AES and RSA encryption techniques, which makes it very difficult for anyone but the hacker to decrypt the files. The encrypted versions replace the old files, and the ransomware displays the extortion message.
How Security Experts Tackled the Ransomware
Actually, it was one security expert in particular that cracked the code to shut down WannaCry before it did, even more, damage: A 22-year old anonymous malware researcher who digs into these problems for a living took a close look at WannaCry and found a significant vulnerability.
Most ransomware has a simple test that it runs when it firsts attacks a computer. This involves sending out a request to a website that doesn’t exist in the real world. This request is designed to fail. Ransomware is often tested in secured simulated environments by security experts looking for a weakness, so it is usually programmed to avoid infected computers in such a simulated network. A simulation wouldn’t route this website request to the real Internet, so the check would pass, and the ransomware would know it was a trap.
The UK white hat hacker came up with a simple solution based on this reaction: He simply bought a real domain for about $10 with the exact same name as the nonsense website that the WannaCry ransomware was programmed to check for. Suddenly, whenever WannaCry checked for the site on any connected computer, it came up positive. The ransomware immediately started thinking that everything was a trap, and it shut down instantly.
Why WannaCry is Still a Problem
Despite the clever solution, WannaCry remains a problem. That’s because hackers can’t resist a successful piece of ransomware, and copycat versions of the attack have already begun. At least two versions have come up with workarounds to the kill switch, including choosing a different target website for the test.
These versions of WannaCry remain less dangerous than the first because 1)we know about them and 2)they were sloppy copies from amateurs, but this doesn’t mean a bigger, badder WannaCry 2.0 isn’t on its way.
The Lessons We Can Learn
Don’t stick with older operating systems! WannaCry was a big problem for two reasons. First, while Microsoft released a patch that would have prevented the issue back in March, far too few people – including organizations that should have known better – downloaded it. That’s why it’s usually a good idea to have automated update schedule enabled, or at least clear instructions after an important patch is released.
Second, don’t get stuck in the dark ages. It took Microsoft a lot longer to create updates for outdated systems like Windows XP, which proved the most vulnerable platform by far for WannaCry. Guess who still uses Windows XP? If you answered, “Governments and lazy businesses,” then you are absolutely right, and they were also the most common victims of WannaCry. It’s all right to wait for compatibility and stability checks, but upgrading to new versions of the OS is important as soon as it is possible.
For more ways to protect your {city} business, contat {company}. Feel free to ask us any specific questions by contacting us at {email} or {phone}.

by Felicien | May 22, 2017 | Education
While it remains unclear exactly how many have been affected by the latest ransomware, aptly called “WannaCry,’ the estimate has already reached more than 75,000 computers in over 150 counties worldwide.
Hospitals, government offices, and high profile organizations are still reeling today after what cyber experts are calling one of the largest cyber attacks ever. This virus, identified as ransomware, seizes control of the user’s computer until a ransom has been paid. The user is given six hours to pay the $300 ransom, with the price increasing every three hours after that.
While it remains unclear exactly how many have been affected, the estimate has already reached more than 75,000 computers in over 150 countries worldwide. A vast majority of these ransomware attacks targeted Russia, but the effects were felt as far as the United States, Taiwan, and Ukraine. A major telecommunications enterprise in Spain reported a freeze on their entire network, as their ransom climbed to almost $550,000.
Who’s at Risk?
The latest in a recent string of cyber attacks was first discovered May 12 and has been linked to vulnerabilities in Windows. Aptly named ‘WannaCry,’ the ransomware targeted Windows XP, Windows 8, and Windows Server 2003 customers who had not yet installed the security update released by Microsoft in March. The National Security Agency (NSA) has received much criticism over the last week, with many blaming their handling of the ‘cyber weapon’ theft last month for the attack. In April, the group called ‘Shadow Brokers’ claimed responsibility for the piracy, but many feel the threat wasn’t taken seriously by the NSA.
While the attack was initially revealed on the 12th, analysts indicate the ransomware software was likely spreading for several weeks, laying dormant, waiting for the kill switch to be pulled. This exceptionally well-written code makes it virtually impossible to unlock encrypted files once they’ve been infected.
In the United Kingdom, outpatient appointments for sixteen National Health Service facilities were canceled and patients were advised to steer clear of emergency rooms if at all possible. China reported PetroChina gas stations were also experiencing difficulties, forcing consumers to pay cash for goods and services. Both countries have reported no evidence of personal information being compromised.
With Russia at the center of a large portion of the attacks, cyber experts indicate that the attack may have originated in Russia. Evidence points to the hacking of an extensive Russian email database as the likely source.
What’s Next?
The ransomware was discovered by a British security researcher, who goes by the name MalwareTech. It was configured to continually contact an unregistered domain that was built into its coding. During his analysis of the attack, MalwareTech registered the domain, which, unbeknownst to him, was what was necessary to halt the ransomware attack from spreading any further.
While Microsoft customers were the target of this attack, all software users are urged to update their operating systems immediately. Windows users who haven’t installed the update Microsoft released in March can prevent an attack on their system by doing so now. Unfortunately, the update won’t help those who have already been targeted in this recent attack. Laptop users should use extreme caution when utilizing public WiFi connections, as the ransomware is equipped with a ‘hunter module,’ which helps spread the virus to anyone on the shared network.
Recent studies reveal that cyber attacks are on the rise, showing no signs of slowing down in the near future. A published FBI report indicates an average of 4,000 ransomware attacks occurred each day in 2016, with an attack on U.S. enterprises occurring once every forty seconds. Businesses and individual users are urged to keep their firewalls up-to-date and configure them to block any malicious IP addresses. Anti-virus and anti-malware programs should also be configured to automatically perform regular scans.

by Felicien | May 22, 2017 | Education
Facebook Ads Manager is child’s play once you get accustomed to the interface. Spend a lot of time trying out each tool to make the most of your Facebook marketing campaigns.
Facebook Ads and Excel easily sound like a match made in heaven. What could be easier than tracking your ads via a convenient Excel spreadsheet? Using this tool along with other resources within your Facebook Ad Manager interface can make charting your ads progress seamlessly. Here are a few basics to get you started with Facebook Ads Manger and tips on using the latest tools.
Grab a Seat and Stay Awhile
Getting comfortable with Facebook Ads Manager is a must. You’ll do everything here: create ads, edit ads, and chart campaign progress. There are four main headings within Facebook Ads Manager: Account Overview, Campaigns, Ad Sets, and Ads. Account Overview is a summary of financials like how much you’ve spent over the past week on ads. While Campaigns, Ad Sets, and Ads are used to create/edit ads and retrieve reporting information. Since there is often a lot of information to process within Facebook Ads Manager, take advantage of the filters available. Options include filtering by date range or by specific keywords. Custom filters can be created and saved to help you find the data you need quickly at a later time.
Creating Ads on Facebook
The rules are pretty straightforward on Facebook for advertising: no adult content, no foul language, no copyright infringement, no misleading content, and no illegal products or services. Poor image quality and poorly worded copy are also common reasons for ad rejections. Take the time to create a polished ad with optimized images before heading over to Facebook Ads Manager.
To start, you’ll want to launch a new campaign. This allows you to tie a new ad set or ad to an existing campaign. Facebook walks you through the campaign creation process so there isn’t a steep learning curve. A campaign is set with an objective in mind before you move onto ad sets. The ad sets you choose will take some research. Select the demographics and placement most relevant to your brand. Ad sets are savable for later use. Design options will be chosen once you enter the Ads screen. This involves choosing your ad’s format and media type. Text and images are uploaded in this section before the campaign goes to Facebook for approval.
Facebook Reporting Tips
Analyzing your campaign’s performance is an essential part of Facebook Ads Manager. If your campaign is stalling, you’ll want to edit the campaign to get better results. You can view results directly from Facebook or use Facebook Ads Manager for Excel or FAME. The benefit of FAME is the ability to import multiple Facebook accounts into your reports. Moreover, you don’t have to mitigate your ad data manually each time you want to view results. With Excel’s refresh function, reports have automatic updating. The reports have plenty of useful data such as ad clicks, page likes, and conversions. Reports also contain the number of impressions for each placement and click through rate. The reports are used to manage your advertising budget since you’ll see total spent and cost per click.
Getting started on Facebook Ads Manager is easy and worthwhile. Promotions on Facebook has a proven track record of being lucrative and you don’t want to miss out on this opportunity.
by Felicien | May 19, 2017 | Education
When someone thinks of spam they typically think of unsolicited bulk commercial email they receive in their inbox. However, the concept of spam started a little earlier than you might think. How far back? How does 1864 sound? Spam in 1864 you say? Yes, in the form of a telegraph, advertising a local dentistry actually. The Telegraph was so much news that the local paper even reprinted the telegraph that was sent to many households, further propagating the message.
More recently, people consider the first spam email coming out of Digital Equipment in 1978 which went to a total of 393 people promoting their latest computer model. You can thank a Monty Python sketch based on a cafe that only served the canned spiced ham SPAM for the origin of the name. Another early spammer was the lawyers Canter and Siegel posting their “Green Card Lottery” message to USENET, a shared messaging system.
What does all this have to do with today? You don’t want to be known as a spammer. There are three ways to attack the spam problem. First off, you don’t want your marketing emails to be classified as spam. Secondly, you don’t want your mail server to be abused where someone sends spam through your hardware. While this wasn’t sent to you directly, your hardware could be blacklisted, thus affecting your own emails. Lastly, you don’t want your employees to respond to spam. There are ways to filter this at the mail server to prevent them from seeing the messages, or at least classify messages as fishy before their opened. Our company {company} can help you to protect your business from being labeled a bad apple in the email business.
Starting with the most important avenue, ensuring your marketing messages get through, there are some best practices to know about. For starters, don’t just send emails directly to your clients. Putting everyone’s email in the “To:” field of a message is bound to cause problems when someone does a reply-all. If you absolutely have to send a message to LOTS of people, it is better to use the BCC (for blind carbon copy) field of a message. Better yet, rely on a mailing list management package like that offered by Constant Contact. Typically, you don’t want to add people to the mailing list yourself. Instead, people should opt-in. More importantly, with each message you send, there should be unsubscribed instructions.
Protecting your mail server is not an easy task. There are some simple steps you can do like requiring that users are authenticated before sending a message, but someone can just spoof the email headers to make it appear messages came through your server. To best protect your server, in 2012 DMARC, or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance was introduced. Combined with the earlier introduced SPF, Sender Policy Framework, this makes sure that any messages appearing to come from your mail server actually came from your mail server. {company} can help you keep up with the latest ways to protect your email servers and thus getting your marketing messages through.
Lastly, it is important to look at the inbound side of spam. With all the talk of Russians hacking servers and the release of inappropriate celebrity photos, most of these attempts are triggered by phishing attacks of targets. You still need to worry about viruses being sent through email, but phishing involves fraudsters sending what look like real emails in the attempt to reveal personal information like passwords and bank account info. You don’t want your employees giving away the farm so that others can then get into your company network or your employees worried about identity theft. {company} can help protect your mail servers from letting these unsolicited emails through.
Contact us at {email} or {phone} to learn more about how we can help you.





