
by Felicien | Jan 3, 2018 | Education
An increasing number of information security officers agree that awareness training for employees is the number-one defense against cybersecurity threats. In fact, the nation’s first Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), Greg Touhill, said that if he had extra money to spend on security, he would spend it training employees. This statement was underscored by Jon Clay at Trend Micro.
Clay reports that “Spear phishing and messaging-based threats tend to be the first attack vector that criminals are using today. They are targeting the employees of an organization first and foremost to get access to that organization’s network. From there, they will laterally move out.”
In effect, his comment highlights the importance of training employees to recognize these threats. Properly trained employees know what to look for. However, just one poorly trained employee can open the door for hackers—And once they get in, they can do irreparable harm.
Your Company’s Data is at Risk.
We were all shocked by the recent security breaches at organizations like JP Morgan Chase and Equifax. If companies with high levels of security can be breached, then what about the thousands of smaller businesses across America?
Although most enterprises increased their budgets for IT security, it doesn’t seem to be having the impact CEO’s had hoped for. When you take a hard look at the job description of most CISO’s, you can readily see the problem. In today’s business environment, IT specialists are required to know everything there is to know about dozens of different devices—And each device must be properly configured and aligned with the overall data system’s architecture.
Data in the Cloud
Cloud technology makes data more readily available to employees—However, it’s also more vulnerable to cyber attacks. This leaves us with the question of whether we can continue to risk our most important data by leaving it out in the open for intruders to find.
Even the world’s foremost experts in this field view the future of digital security with uncertainty. Attacks on prime targets around the globe have been so successful that it requires industries to constantly evolve where cybersecurity is concerned.
Many IT experts believe that one reason for the consistent failure of counter-threat intelligence is the fact that experts are always a few steps behind the attackers. Cyber threats become more sophisticated with each new breach. When critical data is compromised, customer data, financials and intellectual property are freely available to hackers.
The Human Factor
Cybersecurity learning programs now include behavior-modification training. The concept of modifying behavior isn’t new—But applying it to the information technology environment is.
Employees must learn that certain behaviors are unacceptable. During training, they’re shown the numerous tricks that hackers employ—And training must be ongoing in order for it to be 100 percent effective. As cyber attacks evolve, so must our understanding of how to detect them.
Alan Paller, founder of the SANS Institute, along with other security specialists agree that, when it comes to cyber threats, we must address the human factor first. When every employee in a company is fully trained and aware of the many ways attackers infiltrate a company’s data, they’ll be one step ahead of the hackers instead of two steps behind.
CEOs are just as likely to click on a suspicious link in an email as are their employees. Therefore, everyone in an organization should undergo cybersecurity awareness training. From the CEO to the mail room, to every person who has access to a company’s data, all must be informed. It only takes one person to open that cyber door— And once thieves are inside your IT network, they’ll ransack it and take whatever they want.
Cyber thieves are continuously updating their intrusion methods. The latest attacks include effective spear phishing and whaling. They target CEO’s, board members and company leaders.
The quality of their forgery has risen to the point where the threat is almost indistinguishable from the real thing—These emails look authentic. They are so refined that even well-trained individuals can be fooled. The more believable the attack, the more likely it is to succeed. In order to rise to that level of believability, cyber thieves need our help. And they seem to have no problem getting it.
Protect Your Privacy.
As mentioned, the first and best defense against these attacks is education. The second-best defense is to protect your data. There are numerous ways criminals can obtain your confidential information.
Security experts recommend that all discarded paperwork be destroyed using a cross-cut shredder. If attackers can learn just a few key pieces of information about you, they can refine their attack and make it more likely to succeed. Cyber thieves want to know where you bank, your title at work, your favorite hangouts – even the names of close friends and relatives.
Social media makes it easy for anyone to find out who your friends are and even get photos of them. Criminals watch for photos that you post online, when you go on vacation, and more. Once they know you’re away from home and enjoying the beaches in Maui, it’s just a matter of going to your home and breaking a window.
This same philosophy applies to cyberspace as well. We all leave clues around that tell thieves where we shop, where we work, what kind of car we drive and other bits of vital information about our lives. Once they have it, they’ll use it against us in the form of malicious emails.
The Job of Combatting Thieves Involves Us All.
In a world where information is so readily available, the task for CISO’s is now more complex. It requires better and more consistent training for employees and vigilance at every level. With ongoing training, employees can help identify outside risks in their email boxes or across the Internet.
The job of combatting cybercriminals mandates that we take the protection of our data as seriously as we do the protection of our homes and families. It’s not just the responsibility of IT specialists and CISO’s—It’s everyone’s job to guard the “doors and windows” of our network and cloud storage systems.

by Felicien | Jan 3, 2018 | Education
The 2017 Cost of Data Breach Study is an annual study that looks at the cost of data breaches in companies, focusing on different countries such as the United States. This study gives a good idea of the effects a data breach can have on a person and their business. This is the 12th annual study that has been done, and it provides important information. In the 2017 study, 63 companies participated.
Through looking at the effects data breaches have on these companies, a few things could be determined.
The average total cost of data breach in the United States is about 7.35 million USD
There has been a 5% increase in total cost f data breach
The average cost per lost or stole record is $225
There has been a 2% increase per lost or stolen record
A data breach is a very serious thing. It can mean the loss of thousands of sensitive documents that contain private or personal information. Because of this, it can also have a huge impact on your business. It makes sense that the sooner a data breach is detected, the sooner it can be stopped, and the more information you can keep from being stolen. Detection might include forensic and investigative activities, assessment and audit services, and crisis team management. These are all important aspects of keeping your documents and files safe and detecting a potential breach as soon as possible. In 2017, companies were able to lower the number of days before detection from 201 in 2016 to 191 days in 2017. This is likely due to investments in such enabling security technologies as security analytics, SIEM, enterprise-wide encryption and threat intelligence sharing platforms.
After a data breach, it is important to notify those who may be affected. This requires the services of help desks, identity protection services, and legal expenditures. It is very important to let people know when their information has been compromised and to provide whatever services you can for them in dealing with it. This can all be very costly to your business, as the United States has the highest data breach cost, as shown in this years study. Something that may help manage this cost is an investment in data breach insurance. With this insurance, you can offset some of the costs of a data breach. As shown in this year’s study, insurance protection and business continuity management reduced the cost of data breach following the discovery of the incident.
According to this year’s benchmark findings, data breaches cost companies an average of $225 per compromised record – of which $146 pertains to indirect costs, including abnormal turnover or churn of customers and $79 represents the direct costs incurred to resolve the data breach, such as investments in technologies or legal fees. These costs add up and can have a very real impact on your business. For this reason, it is important to understand where data breaches come from, and what you can do to not only protect yourself but also lower the cost of the issue.
In the 2017 study, it was found that 47% of companies participating in the study identified the root cause of the data breach as a malicious or criminal attack. This means that it was more than human error or negligence that created this problem. The average cost of a malicious attack was approximately $156, compared to $126 where human error was concerned. To lessen the likeliness of these attacks, as well as the cost to your business, it is important to invest in security analytics as well as the recruitment and retention of informed personnel.
In comparison to other countries, the 2017 study shows that the United States experienced a higher number of breaches, which can be very costly. Other countries such as Australia, Germany, and France, were able to reduce the cost of data breaches. In the United States, the cost of a data breach can span over multiple systems. This year the cost of a data breach increased by nearly 5 percent. Much of this cost was due to the churn and loss of customers. Looking at how other countries were able to reduce the cost of data breaches by retaining customers gives a great hint at something that could potentially help businesses in the United States to lessen their costs. Four categories that influence data breach costs have been put out with this study, they are:
Compliance failures
Extensive use of mobile platforms
CPO appointment
Use of security analytics
Compliance failures and extensive use of mobile platforms increase the cost of data breaches by almost $26 million while appointing a CPO and using security analytics reduce these cost by about $11 million. This shows the importance of working towards implementing systems that reduce costs, because they may not have as much impact in reducing costs as other issues to increase your costs.
Protecting your business and the information it has been trusted with is always the main goal of any company. For this reason, data breaches are a very scary, but real, though. It is important to know what causes data breaches, like malicious software, as well as the different ways you can protect your business, like implementing security analytics. The 2017 Data Breach Study provides all the necessary information one would require to update their systems, and stay informed about potential online threats.

by Felicien | Jan 3, 2018 | Education
Scam phone calls aren’t a new thing, but today’s scammers are now bolder and more sophisticated. In 2010, more than 84,000 people reported phone-related scams to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Scammers can spoof phone numbers from your local area code or a number that you recognize. When they call, you might think it’s your mother or brother—You wouldn’t know the difference until you picked up the phone.
Scammers will even call pretending to be your child, your spouse, or another family member – speaking quickly as if they’re in a hurry and need your information right away. If a scammer called your mother and spoofed your number, would she know it wasn’t you if the caller was speaking fast and in a panic?
Caller ID Spoofing is the process of changing the caller ID to any number when you want to hide the real number. To transmit the caller ID, the spoofer needs three pieces of information: the number you’re calling from, the number you’re calling to, and whatever number you want the display to save. When a customer receives a call, the caller ID gets transmitted between the first and second number.
(You can view an NBC report about spoofing here.)
According to Ajit Pai, Chairman of the FCC, they are empowering phone companies to block robocalls that appear to be spoofed with no real legitimate purpose. They’re taking aggressive action against these callers, and are working to find better technological solutions to guard against fake calls.
Apps such as Mr. Number and TrueCaller can help you determine the difference between spoofed and non-spoofed calls:
TrueCaller works as a caller-ID app, albeit a beefed-up, superpowered one. It tells you who the caller is, where they are from, and who they might be. It prevents calls from telemarketers and spam callers. It pulls the numbers and contact info from its users so all the numbers stored in your contacts will end up in the TrueCaller database. Currently, this database is home to two and a half billion contacts.
With Mr. Number, you can narrow down your desired specifications in the settings menu. You can block specific numbers, entire area codes, numbers not in your contacts, calls you suspect are spam, and intercept calls from private/unknown numbers and review them later in your recent call list.
Here are some tips for dealing with scam or spoofed phone calls:
Don’t Give Them Anything. These scammers are hunting for information. The best thing you can do is to tell them nothing. Simply hang up. Any bit of information that you provide could be used to separate you from your money or identity.
Don’t Call Me. If an organization, charity, or group calls you uninvited, they probably aren’t who they say they are. Even if your caller ID looks legit, it might not be. Caller ID spoofing is becoming more common. Rely instead on your instincts. If it feels wrong, it probably is.
I’ll Call You. If the caller insists that they speak with you right away, tell them that you’ll call them back directly. At this point, some scammers will offer you a phone number as a way to verify they are who they say they are. Don’t call this number. You’re better off looking up the number yourself. Or, if it’s a company you’ve done business with before, like a utility company, call the number that’s listed on your monthly bill.
Keep Alert. Even if you’re the one initiating the call, you could still be at risk. When calling a company that you don’t know, before talking with them, do some homework. Look them up with the Better Business Bureau, check their website, and research them online. You can even ask them to mail you some information. If they’re legit, they’ll know where to send it.
Don’t Be Rushed. The scammer might try to hurry you into making a decision. This is often employed by scammers who are spoofing a number that you know. Don’t let them rush you into giving up vital information. This is how they get you to slip up and give them what they want.
Be Part of the Solution. If you’ve received a call that you suspect is a scam, report it to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) at 877-FTC-HELP (877-382-4357). If you don’t report it, someone else may fall victim to the scammer.
Spoofing a phone number without permission is illegal. In Canada, the CRTC suggests that victims file a complaint if they’re sure the caller ID was spoofed by a telemarketer or conman.
by Felicien | Jan 2, 2018 | Education
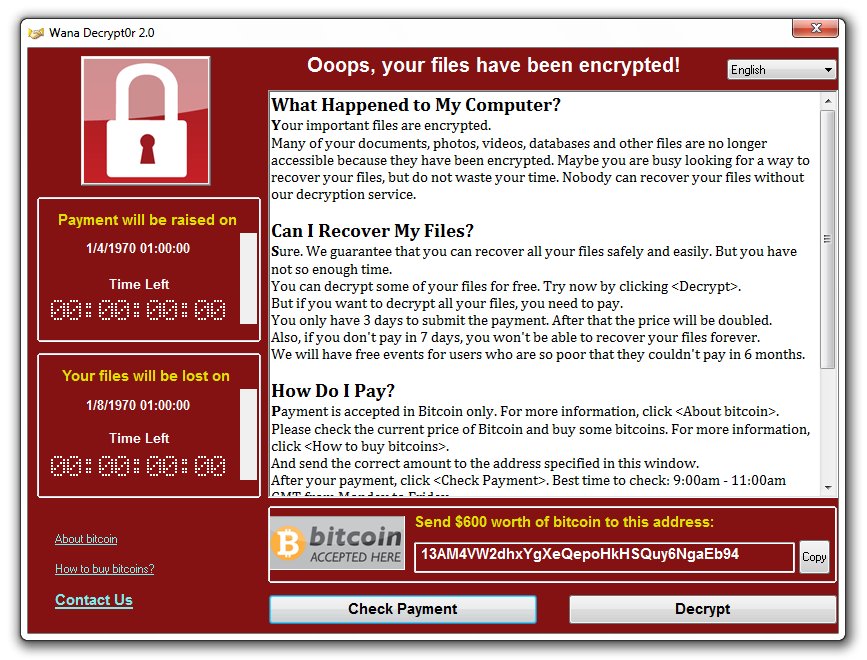
Ransomware is now a household name, and there’s no going back. Even though cybercriminals have been using ransomware for years now, it wasn’t until the global WannaCry attack that awareness reached critical mass.
Doctors and nurses went to work as usual last May in the UK’s Central Manchester University Hospital, but when they went to turn on their computers, all computer systems began crashing. Messages began to pop up on their computer screens demanding $300 in Bitcoin in exchange for restored access – the WannaCry ransomware had struck.
Targeted Manchester hospitals claimed that no patient info was compromised, but they did have to suspend services. The BBC reported that other hospitals in London, Nottingham, Hertfordshire, and Blackburn had also been attacked and that some phone systems went down for a period of time. Doctors and nurses were forced to use pens and paper to keep track of patient information. Once medical organizations across the UK had realized what was happening, some of them disconnected from servers at the National Health Service to try and avoid being attacked.
Exploiting Microsoft’s Operating System
This is just one of the many stories that have unfolded over the last year where large organizations were targeted with one of the largest ransomware attacks in history, named “WannaCry”. Though experts did not know this at the time, WannaCry is a ransomware cryptoworm developed by North Korea and aimed at Microsoft operating systems.
Though it seems unbelievable, there have now been more than 100 attacks like this across 150 countries just this past year. Most anti-virus software makers have scrambled to get ahead of these attacks. Once Microsoft’s experts had found that the attacks took advantage of a Windows vulnerability, they quickly released patches for computers running all versions of the operating system, including older versions such as Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and Windows 8.
Kurt Baumgartner, at the security firm Kaspersky Lab, explained how effective and how quickly WannaCry ransomware can strike.
“Affected machines have six hours to pay up and every few hours the ransom goes up,” said Baumgartner. “Most folks that have paid up appear to have paid the initial $300 in the first few hours.”
Other experts in the field of Cyber Security found evidence that these attacks were made using a variation of the malware called, “Wanna Decryptor”. This program is a Trojan virus that utilizes AES-128 encryption to make all files inaccessible to users.
Though many of the ransomware attacks were launched against the UK, Russia, Taiwan, and Ukraine, global firms like FedEx have come under assault as well. Officials from Europol said that the attacks were of an “unprecedented level and require international investigation.”
Meanwhile, China reported a massive attack against PetroChina that took some time to resolve; as a result, customers were forced to pay cash at all PetroChina gas stations until the ransom had been paid.
Spain also reported an attack against Telefónica, a large telecom organization. Their experts were able to determine that the attacks were spread through a vulnerability called “EternalBlue.” Their IT department quickly created a patch to prevent the bug from spreading.
Controlled Folder Access For Windows 10
All of these attacks were launched against Windows-based systems, leaving IT security experts at Microsoft to take quick action to develop and release patches and other tools to stop cybercriminals. The fall updates to Windows 10 included many new improvements aimed at providing a much higher level of protection. One of these, known as Windows 10 FCU, has proven especially useful. Also known as Controlled Folder Access, this update protects files and folders from ransomware attacks using a simple methodology.
The exploit is based on the fact that most Windows programs have access to all files and folders on a computer system, which made it much too easy for hackers to gain access to those files and wreak havoc. Unrestricted access to files and folders might be convenient for users, but it opens the door to virus and ransomware attacks.
Customizing Your Operating System
Though many users are not aware, Windows gives you the ability to greatly customize your operating system, including the capability to take action to protect your data from hackers. Using Controlled Folder Access, you can modify access to your important data, so that these files are given an extra layer of protection. If any program tries to modify files that have been placed in the “protected folder”, they will be blocked. This feature is found in Windows Defender.
Follow these steps to enable Controlled Folder Access on your computer:
Type Windows Defender in your start menu. This opens the Windows Defender Security System.
Navigate to the left panel and find Virus and Threat Protection. If it isn’t listed there on the left, then type “virus and threat protection” in the settings search box at the top left.
Click on Virus and Threat Protection Settings. This may appear in a new dialog box or on the right side of the Virus and Threat Protection page.
Scroll down and find “Controlled Folder Access”. Toggle the button to “On”. This enables the Controlled Folder Access feature.
Granting manual access to programs
The most significant drawback to using this feature is that some of your favorite apps or programs may be blocked. The solution is simple: Manually grant access for these programs. Just below the toggle button, you’ll find a link called, “Allow an app through Controlled folder access”. Click on that and a new dialog box appears. Now click the “Plus” sign out beside “Add an allowed app”.
The familiar “Open a File” window on your computer will automatically open, giving you the ability to click on whatever file, folder or program you would like to exclude. Navigate to the EXE file and then click on “Open”. You have successfully added this program to your exclusions list.
This works for all your favorite programs like Photoshop, Dragon Naturally Speaking, and Quickbooks. Please note that Windows has its own list of “safe” programs that are already included, so there’s no need to grant manual access to programs like Excel and Publisher.
For more information about the latest IT security threats and how to protect you and your business against them, get in touch with our team of cyber security experts.

by Felicien | Jan 2, 2018 | Education
Did you know that in 2016, IBM found that 60% of all cyber attacks were carried out by insiders? Of these three quarters were due to malicious intent, and one fourth due to negligence or error.
Accidents: According to Verizon’s 2016 Data Breach Incident Report, accidents accounted for 30% of security incidents. In many cases, employees haven’t been educated properly on cybersecurity best practices. They open phishing emails and click on malicious links that expose sensitive data.
Negligence: This is when employees try to circumvent the policies you’ve put in place to protect endpoints and valuable data. For example, they might try to share work on public cloud applications so they can work from home. There’s no malicious intent, but by doing this they expose your data to dangerous actors.
Malicious: Unfortunately, there are times when employees are motivated by financial gain and reveal your confidential data. For example, a disgruntled employee who was recently terminated might extract sensitive data on his/her way out and either sell it or release it publicly.
What You Should Do
As you look to how you should secure your IT environment as a whole, there are two main questions you should ask:
What departments or people within your business pose the biggest threat?
What processes can you put in place to minimize this risk?
Ultimately, it’s not the people in your organization who are the least reliable that you should be concerned about. Instead, you should focus on the work employees do, the technology they use, and the data they’re responsible for—data that would be appealing targets for hackers and cybercriminals.
The following are the three departments that experts suggest you focus on:
The IT Department
IT staff often possess greater access rights than do other departments. They have access to business-critical data through the IT systems they manage and control. This makes them a prime target for cybercriminals. According to the 2017 Balabit Report, 35% of IT professionals consider themselves as the biggest security risk to their organization.
Finance
Your financial department poses a risk because of the large sums of money they handle. They are often targets of phishing attacks where criminals try to get them to transfer large sums of money, and bypass normal accounts-payable procedures and controls. Unfortunately, not all employees who have access to funds are up-to-speed on these fake payment requests. It’s important that they are taught to maintain rigid purchasing processes. A simple call or email can expose your company to theft.
The C-Suite
Your CEO, CTO, and other top executives are always on the go and require access to 100% your company’s information and data. A mobile workforce is the trend of the future, and company leaders have been working from remote locations and off-site meetings for years now. However, 93% of tech leaders surveyed said they were concerned about the security challenges presented by a growing mobile workforce.
Threats to Small Businesses
As a small business owner, your focus may not be identical to the departments described above. Simply think of the places where data and money are transacted, and what networks those workers are most often connected to.
To mitigate these risks, be sure to implement the following strategies in your workplace.
Treat security as a culture, not a policy. Cybersecurity must be a company-wide initiative and “all-hands-on-deck” strategy. It shouldn’t be the sole responsibility of just a few individuals or a particular team—Although it might be okay for one department or person to lead it.
Educate, train, repeat. Bring all employees into the conversation, make sure they stay up to speed, and consistently revisit this. The tricky part about IT security is that it’s ever-evolving. Hackers are constantly developing new ways to gain access to information that doesn’t belong to them. Staying up to date on these changes, tweaking company policy to cover all the bases, and distributing updates through security awareness training programs must be a top priority for organizations today.
The Better Business Bureau has a great list of starting points if you’re looking for a checklist. If there’s no one individual who can lead the implementation of these strategies, consider contacting your IT provider to for assistance and training.
by Felicien | Jan 2, 2018 | Education
W-2 Phishing season is about to begin – without the right IT security services, your business will be left vulnerable.
You and I know that effective communication with co-workers and clients is crucial, but are you sure your employees are practicing safe email and messaging conduct? If you don’t already have the best technical security services, your answer is probably, “I’m not sure”, right?
Cybercriminals are smart – they adapt quickly and continually come up with new ways to take advantage of businesses like yours. A popular tactic among hackers today is “phishing”, a method in which they send fraudulent emails that appear to be from reputable sources in order to get recipients to reveal sensitive information and execute significant financial transfers. With only a surprisingly small amount of information, cybercriminals can convincingly pose as business members and superiors in order to persuade employees to give them money, data or crucial information.
At this point, phishing attempts are nothing new, but without the right computer security services, you can still fall victim to a common phishing scam. This is especially a danger in the coming weeks when phishing will be primarily used to target W-2 data being processed for your employees during tax season.
This is nothing new. Over the past few years, cybercriminals have been very successful during tax season, executing social engineering campaigns against thousands of targets in order to access and steal valuable W-2 data. By sending phishing emails to unsuspecting workers in the payroll and HR departments in target businesses, cybercriminals have caused extensive damage, leaving companies like yours liable for fraudulent tax returns, identity theft, and class action lawsuits.
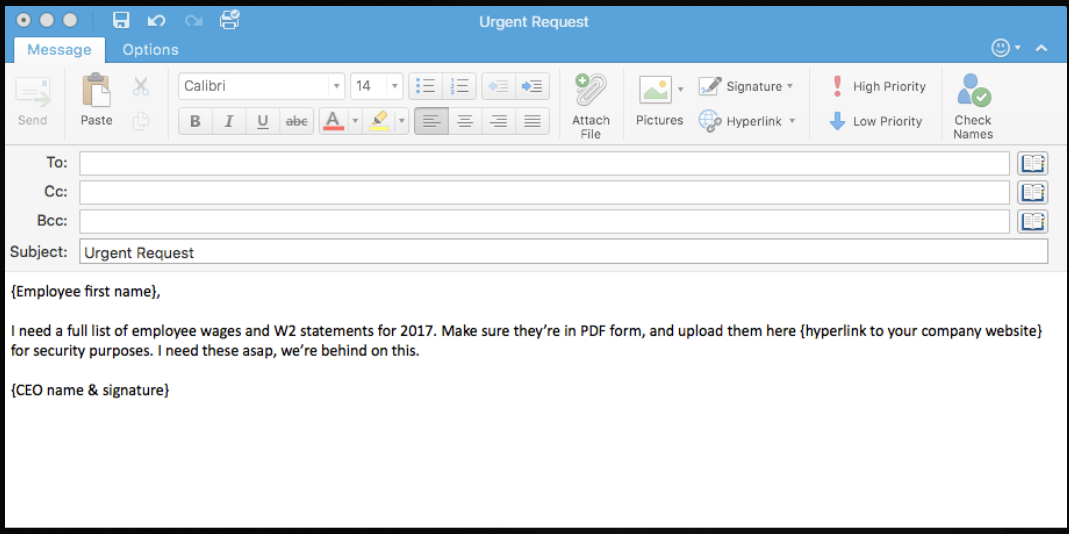
What does a W-2 Phishing Email Look Like?
As dangerous and damaging as these types of social engineering scams can be for you and your employees, the good news is that they are avoidable – if you know what you’re looking for. The key identifiers of a phishing email like this include:
Sender: Typically, the email will appear to come from a high-level executive or someone that the target employee wouldn’t want questions or ignore. Often the cybercriminal will go so far as to mimic the executive’s email signature to enhance the authenticity.
Request: The email will request W-2 or other tax information to be sent via reply, sent to another email address, or to be uploaded to a server.
Timeframe: The cybercriminal will likely try to create a sense of urgency so that the target doesn’t have time to think about the request or confirm it through other means.
Once the user’s email, password, and other information have been entered into the fraudulent website, the damage is done. The hacker can then take the information and do even more damage with it. It’s the new and constantly evolving cybercrime threats like these that make network security services so vital.
The key to phishing methodology is that it doesn’t rely on digital security vulnerabilities or cutting edge hacking technology; phishing targets the user, who, without the right training, will always be a security risk, regardless of the IT measures set in place. The reality is that small and medium-sized businesses like yours are put at great risk if you don’t have cybersecurity services.
What Can You Do About Phishing?
So what’s the answer? What can the average business member do to keep themselves and their company safe when criminals are employing such deceitful methods? In addition to equipping your business with the best technical security services, you should also be sure to educate and test your employees on IT security best practices and knowledge. Make sure they understand the following:
Never give out private information: The trusted institutions with which you do business will not ask you for your private information. They already have your account numbers, social security number, and your passwords. They won’t have any good reason to ask for it again, right? If an email from a superior or external contact asks for that info, it is likely a scam, so be sure to confirm the request by phone or in person.
Never click on a link before you hover over it with your mouse: If you hover over a link with your mouse, your computer will show you where that link is actually taking you. Many times, criminals will give you what looks like the right link (such as www.YourBank.com) but when you hover over the link with your mouse it actually will show something different (such as
www.YourBank/2340937fvt5.com). If the link is not as advertised, then don’t click.
Always check up on unexpected email attachments. If you get an email from someone you know with an attachment that you weren’t expecting, give them a call or send them an email to confirm that the attachment is from them and is legitimate before you open it.
How Can You Be Sure Your Employees Know About Phishing?
The best way to ensure your employees know how to deal with a phishing threat is to test them. Allow us to help. We’ve prepared an example phishing email template that you can fill out and send to employees in just minutes to test their knowledge of phishing threats.
Check out this screenshot of an effective test email you can send to your employees to prepare them for the W-2 phishing season:





