
by Felicien | Jan 23, 2018 | Education
When Facebook first launched back in 2006, the world was introduced to a brand-new way of communicating. Friends and family that lived hundreds and thousands of miles away from one another now could bridge the distance.
If you have been living under a rock for the last 12 years, Facebook is a social media company that allows family and friends to share pictures, life updates, and any random thought. It also makes you the star of your show, as it gives people a platform to let their voice be heard.
Fast forward to 2018, a little over ten years since the launch, and Facebook has become a household name with over 1.37 billion people logging onto the social media giant daily. However, it is also a place where third-party businesses, sites that post funny pictures and memes, sell their products or distribute news articles, and advertise to Facebook’s billions of subscribers–but not for long.
Here are a few facts that advertisers should be afraid of 42% of them report that Facebook is critical to the success of their business. Their target audience, people, ages 25-34, are the same people that make up the majority of Facebook users. This is the prime target demographic for many businesses’ marketing efforts, and they rely on Facebook to engage these critical consumers.
The California-based company has kept revenue growth throughout the years by selling more and more advertising in its news feed. However, new changes will scale back advertising and bring lesser visibility to their posts. What you will see is more posts from friends and family, especially those that have incited debates in the comments. Prioritizing what friends and family share are Facebook’s way to help people spend time on the site in a more meaningful way. In fact, last week, Mark Zuckerberg, co-founder of Facebook, said his resolution for 2018 was to “fix” the social network.
Besides the influx of advertisers popping up on Facebook, social media has come under fire in recent years for the impact it has on people’s mental health. Several studies were conducted about the effects on people who use sites such as Facebook. The Journal of Experimental Psychology revealed that using the website, even for just 10 minutes a day, had a harmful effect on our well-being.
People have become addicted to smartphones and often use them to keep up with social media. They put these sites at our fingertips 24 hours a day, no matter where we are or what we are doing. Research goes on to suggest that Facebook can make people feel isolated and sad. Even when looking at feeds from family and friends, people are comparing lives, which can lead to depression and a sense that they are not living up to what others are doing. Teenagers are particularly prone to “Facebook depression” as they try to fit in with their peers, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
However, other researchers believe the way people react to Facebook depends on their personality. If you are already plagued by anxiety or are unhappy with your life, then seeing other people having fun would more than likely deepen your feelings of inadequacy. If you are self-assured and happy with your life, then seeing the good things in a friend or family members life would make you happy, too.
While speaking with the New York Times, Zuckerberg noted if people begin to feel better while on the site, that Facebook’s business, and its users, will benefit: “I expect the time people spend on Facebook and some measures of engagement will go down…However, I also expect the time you do spend on Facebook will be more valuable…The world feels anxious and divided, and Facebook has much work to do – whether it is protecting our community from abuse and hate, defending against interference by nation states, or making sure that time spent on Facebook is time well spent.”
Facebook may care about their users’ wellbeing, but another reason for the changes stems from a growing backlash from academics and lawmakers, and pressure from regulators in the U.S. and overseas about how social media may be leaving us depressed and isolated. Facebook would certainly rather make changes under their control than be forced to make changes according to regulators. Nor do they want disappointed users to leave for different platforms.
So, just how does Facebook plan to make these changes? They will reconfigure algorithms that guess what you may be most interested in. In the early years, Facebook’s news-feed ranking system was based on three things- Affinity, Weight and Time Decay. According to Marketing Land, affinity is how close the relationship is between the user and the content or its source. Weight is what type of action was taken on the content. Time Decay is how current the content is or how recently it was posted. While those three items are still included, Facebook’s current news feed algorithm considers over 100,000 other factors as well.
While he recognizes that Facebook may never be entirely free of harmful influences, Zuckerberg says that the company currently makes “too many errors enforcing our policies and preventing the misuse of our tools.”
What else does the future hold for Facebook? With Zuckerberg at the helm, it is sure to be bright. When people close to him speak of his skills, it is always impressive. One of his key attributes is to keep moving forward and getting better. One PR rep for Facebook revealed that “He notices things that are broken before anybody. To say he is actively involved is an understatement.” His peers note his persistence and devotion to improving Facebook and himself. Zuckerberg “is a total inspiration in how much he cares about his work and in how hard he works,” says Chris Cox, who joined the company as a software engineer and is now chief product officer. “For all of us who work with him, it is like, Man, he is so good at improving.”

by Felicien | Jan 22, 2018 | Education
Cybersecurity is a big, scary word with big, scary implications. The word conjures mental images of a dark room and someone in front a dimly lit computer. The black screen flashes green and is dotted with lines of code entered by a nameless, faceless “cyberterrorist” – a hacker – with a smirk and an evil laugh. Are hackers merely the digital age’s version of a pirate ship on the high seas, with the sought-after treasure in the updated form of digital profit?
The reality, though, is far scarier: data security is big business, and with every business venture comes big risk. You’ve worked hard to get where you are. Your business is growing, and the truth is this makes you a target. Any vulnerability is an unfortunate side effect of success, and with this comes fear – fear of losing everything you’ve built. Hackers spend hours trying to uncover these vulnerabilities and exploit them, sometimes for profit or ransom or just to cause damage.
How do these hackers do this? Hackers obtain access to a computer and plant “malware,” malicious software, like a virus or another executable program. The purpose of these programs varies, but the shared nature is they’re not meant to help anyone but the hacker. In some cases, the idea is to have this malware operate undetected – but not always.
One of the most famous hackers today is “Anonymous,” an international group that has become well-known for DDOS (distributed denial-of-service) attacks on government, religious, and corporate websites.
Every day, hackers are finding new ways to attack, and are sometimes successful simply because those they attack just haven’t yet applied available security updates, called patches. A patch is a corrective action to address a specific vulnerability.
A critical patch update – a CPU – is a series of patches released at the same time that resolve security vulnerabilities. Often when a CPU is released, it’s in response to a discovered vulnerability, sometimes hackers already exploiting the weakness. Organizations will accompany a CPU with a statement of disclosure of these vulnerabilities and the solution within the CPU. No matter the reason, a CPU shouldn’t be delayed.
Oracle
For example, Oracle recently released a patch for select products, including its WebLogic Server. Oracle discovered a vulnerability affecting WLS Security, allowing attackers to exploit access resulting in a successful takeover of the server.
For what is considered to be the industry’s best application server with features for lowering operational costs while improving performance, this vulnerability reflects an urgent need for users to update. In Q4 2017, Oracle released a security alert notifying customers of affected Oracle products and strongly advised that the CPU released in October be applied immediately.
Oracle patch CVE-2017-3506 addressed WebLogic’s “Web Services” subcomponent
Oracle patch CVE-2017-10271 addressed WebLogic’s “WLS Security” subcomponent – a critical Java deserialization vulnerability
Impacted WebLogic versions: 10.3.6.0.0, 12.1.3.0.0, 12.2.1.1.0, or 12.2.1.2.0
More details on this were not publicly available until December when Oracle announced that the vulnerability would have allowed unauthorized users to gain remote access and takeover.
How was this discovered?
Logically, hackers placed a script on affected servers that unintentionally “killed,” or prevented the servers from functioning – possibly even alerting some of the intended targets of the attack before the attack had the chance to deploy fully.
In this specific case, one widely-shared thought is that hackers were exploiting this weakness to install software that mines bitcoins on the affected servers. One element that makes this situation unique is that only limited coding knowledge was needed to make this hacking effort a success if fully and properly deployed.
What is bitcoin mining? Specialized software is used to solve complex math problems in exchange for an amount of bitcoin currency. Why does this matter? If this activity is taking place as a result of a hacker accessing your server, and this hacker now has control of your data, everything is at risk. In most cases, bitcoin mining on a regular computer didn’t allow the generation of enough of the currency to offset the power consumption cost, making this an unappealing option for bitcoin miners. If you read between these lines, hacking someone else’s machine is a better target since the hacker isn’t paying the power bill!
Imagine if, instead of just one computer for a single user, you utilize a cloud-based solution for your entire business, and a hacker was able to access your incredibly powerful resource for their benefit – compromising your data. What would be the impact on your business if this data library became lost?
What does all of this mean?
First, it means we strongly recommend a thorough security review to protect yourself, your business, and your data.
Next, it’s vital to remain vigilant after a patch is installed, and investigate further. If one hack attempt is successful, more importantly by a less-sophisticated hacker, then a more skilled “cyberterrorist” is likely in a better position to gain even stronger control over your system.
Is there an upside?
The good news is that cybersecurity is an increasingly critical component of today’s business model, and the industry is growing – as is the pool of candidates and the knowledge base within. The evolution of cybersecurity is a byproduct of the ever-evolving world of technology, and those organizations that focus on the latest trends and the newest solutions are supporting the strength of the field.
Standards are being established across the technology industry, laws are being written to protect digital and intellectual property, and crimes are being prosecuted.
Precedents are being established with which to fight cyberterrorism and hackers, in numbers great or small.
What can you do?
The best thing you can do for your business – and thus, yourself – is to employ a top arsenal of experts that can aid you in protection against cyber attacks. Remember that even the best efforts need ongoing support.
The key to long-term success is to work with experts that understand your needs and the nature of your business in such a way that there is a seamless relationship: Where you end, your “cybersecurity expert” begins, and eliminates any vulnerabilities. When customers ask you what the secret of your success is, you can honestly answer that you only work with the best – and that’s the best position to be in for the future.

by Felicien | Jan 22, 2018 | Education
There’s no doubt that Big Data, Data Mining, and Machine Learning have changed every industry on the planet. Recent political campaigns were won by experts who knew how to use all data available regarding key factors. Many were surprised to learn how certain types of information could guide a political campaign down the pathway to a big win.
Data analytics now used in many industries
Data analytics has been used in the field of sports for many years. This is perhaps one of the first industries to fully embrace this concept. All professional sports organizations use volumes of data to understand past performances of rival teams. They analyze every bit of the information available to discover a competing team’s weaknesses. Then they use that information to build an arsenal of both offensive and defensive strategies.
It’s natural that the legal profession would want to gain the upper hand in this same manner. And, that is exactly what’s taken place in the last few years. Now we have teams who are experts in both technology and the law. Using the most sophisticated tools available, they decipher every morsel of legal information, including trial outcomes, court decisions, witness testimony, precedents and much more. This gives their side the competitive advantage.
However, the issues that the legal system faces differ a great deal from those of other industries. A sports team analyzes things like various plays and the results of those actions. In the legal field, every trial generates huge amounts of data. From the trial transcripts to the expert witnesses, the sheer volume of data sets the legal field apart from most other industries.
How legal data differs
Last year, in the US alone, there were over 350,000 cases brought to court. And legal data is highly complex. It contains legal nuances that are hard to explain to most people, much less a computer program. Trial outcomes typically occur as a result of hard evidence, but sometimes they are a result of emotional juries. Since juries are made up of human beings, it’s very hard to predict with accuracy what they will do in any given situation. That’s the goal of trial science.
In the past, America has held very public trials for popular athletes accused of crimes like assault or even murder. All the evidence might point to the suspect being guilty. And yet, the jury had a previous emotional connection with the athlete because they enjoyed watching him play sports. Even with overwhelming evidence of guilt, the jury ruled that he was innocent.
How do you explain that type of irrational thinking to a computer? How will artificial intelligence deal with anomalies like this? These are just a few of the questions facing today’s data-driven attorneys. Though big data offers a world of opportunities, it also represents a substantial challenge even to the best legal researchers.
How to produce the richest data
Today’s legal technology experts are continuously adding new information to their databases. Every trial and verdict is a new piece of information that the AI will use to build its intelligence platform. In fact, millions of pieces of data are added daily to the repository. These massive blocks of data require high-speed processors. Much of this is accomplished using data-parsing technology.
This process cleans raw data, refines and enhances it, and structures the data so it offers maximum insight to users. For instance, one program allows searchers to look at the decisions specific judges made in the past. This helps them build a profile of that judge’s legal philosophies. With great accuracy, these programs can predict how a judge will rule in a certain type of court case. Imagine being able to know with some degree of certainty, how a judge might rule on a specific case before the trial even begins.
Endless possibilities
The possibilities this technology provides are endless and offer a wealth of valuable information to attorneys. As the future unfolds for the legal field, experts believe that advanced technology will be used in every part of the law.
Of course, today it’s being used primarily by legal teams that want to win cases. There are often substantial financial reasons for wanting to win a big case. Today’s attorneys understand that clients are looking for the best team of lawyers. They want to work with the brightest people–winners. But, there’s more than just money on the line; a law firm is building its reputation as well. They want to build their brand to the place where their name is a byword in the legal world.
Refining the legal world
These are natural reasons for wanting to win at anything. However, many experts believe the future of legal technology holds much more than this. They believe the legal field can evolve into a much more fair, accurate and profitable industry. As a society, we can begin to get things right when it comes to verdicts in big cases. We can move past the place where known murderers are freed over a technicality. This is not a pipe dream for many in the legal field, it’s a destiny that must be achieved for our legal system to continue moving forward.
Perfecting a complex legal system
From making new laws to enforcing old ones, data mining and machine learning have the potential to show us where our society’s legal system has failed in the past. We can clearly see what has worked and what hasn’t. We can use this knowledge to move forward in a better direction. Unfair laws could be changed, and unfair verdicts could be a thing of the past.
That’s the hope of every reputable attorney. Today, we may use data mining and AI to gain a better advantage in a trial. Tomorrow, we may use them to mold our legal system into a fine-tuned instrument that delivers correct verdicts every time, and at a third of the cost.
by Felicien | Jan 21, 2018 | Education
The Internet of Things (IOT) is simply the connection of devices to the internet (and/or each other) with an on/off switch. Your phone, tablet, and laptop computer are all connected to the internet, and for some each other, with an on/off switch. But this isn’t restricted to those types of devices. Since it’s anything with an on/off switch, it opens up to your car, your alarm clock and even your refrigerator are connectable to the internet and can talk potentially connect with each other.
The IOT is a network of connected devices to other devices, devices to people and people to people. There will potentially be more than 26 billion devices connected by 2020. Can you imagine? How great would it be if you’re connected car could send an email to work letting them know that you’re going to be late because of traffic on the highway? Your fridge already sends you notices when you are out of things.
The IOT allows for endless possibilities of connections across an endless supply of devices. There are so many possibilities that we haven’t even figured them out yet. This makes the topic something to talk about and something to watch. But along with the opportunities that IOT presents, there are also challenges, too. It is no wonder that when discussing this the term “security” comes up a lot. With the billions of devices all connected, how likely is it that someone finds a way to hack into your smart fridge and gain access to your network?
Also, many companies will be producing loads of sensitive data from all the devices that they have connected to the IOT. This opens up companies to more cyber threats, not to mention the issues of data sharing and privacy. There will come a need to store, track, and analyze all this data that is going to be generated.
Speaking of data, the future of the Internet of Things has already arrived. It’s the virtual assistant. Google, Alexa, Cortana, and Siri are all virtual assistants from four different companies (Google, Amazon, Microsoft and Apple). These devices were created to make certain aspects of our lives easier. They can order stuff for us, control the house lights, alarms, TV and so much more. They are always listening and always connected, taking in everything that they hear and analyzing the data.
This virtual assistant gives you convenience and saves you time in your daily routine. At the same time, it is sending the parent company of the device (Google, Cortana, Alexa, and Siri) all the data from your life. They know what you eat, what you read, what you watch and more. All this data is quantified and analyzed so that it can be used in any way that they can within their terms of service. You see a small dose of this through ads in your Facebook feed and emails from Amazon.
Your smartphone keeps track of where you go and where you’ve been. It connects to your virtual assistant and to your computer. Imagine that connectivity between computers, phones, and tablets in your business. Some professions are already utilizing this kind of connectivity, making their work easier and at the same time producing more data that needs to be stored and analyzed. This will inevitably require more server space and more speed from the network, all of which requires more work and time for the IT department or managed service provider.
With hackers finding more ways to get at your data and make money from cyber attacks on businesses, is all this connectivity good for business? Let’s look at a few of the ways that IOT can impact your business:
Data
With customers connecting in new ways and more often, there will be plenty of data that needs to be stored or quantified. Smart devices will be able to track customer behavior and maybe even learn from it. This data could be used to personalize ads and suggest orders in new and interesting ways.
Inventory
The freedom of the “smart house” will now translate into the “smart warehouse.” You’ll be able to track inventory automatically, freeing up your workers for other tasks. You could track an item from warehouse to the customer to reorder all through the internet.
Remote work
If your business doesn’t deal with physical inventory, that could free up your employees to work remotely. With their devices connected to computers or servers back at the office, they will work easier and more effectively from the field. It is said that employees work better when out of the office, so this could improve morale, which in turn affects the bottom line. A win/win.
Speed & accessibility
Having access to the things they want easier and more efficiently, customers will be ordering faster, cutting down on the amount of time it takes to get what they want. This may even result in the customer wanting delivery faster since the ordering process is so much easier. Since any third party shipping company you may use will have the same tools as you, they will be able to help you serve that customer even faster.
Efficiency & Productivity
Getting things done faster could lead to better productivity and more efficient operations. This would allow you to cut down on the number of people you employ or maybe you can change some things in a new aspect of your business, allowing your business to grow in ways you wouldn’t have been able to before.
You might be able to cut some workers, but then you might also want to hire new ones that could fill the need for IT service. Or take that money you save from fewer workers and invest it in hiring an outside IT firm such as {company}. Helping you manage this new frontier of connectivity is what they do, so give {company} a call and find out how they can help you grow your business today.

by Felicien | Jan 19, 2018 | Education
Technology is advancing faster than ever before. We can now connect and create on a broader scale than many ever thought possible. However, as our technology advances, people are questioning the security of these cutting-edge systems. While most of our private and confidential information is thought to be protected, the truth is disheartening.
Hard drives have been replaced by the easily shareable cloud, and its improvements continue to help us send, share and store documents. While we might not fully understand the cloud, we trust it. In fact, most companies today use cloud-based email systems to communicate with others. However, hackers have found ways to get into these email systems and encrypt documents, so we can’t access them.
This scary new ransomware strain was created by good hackers, and unfortunately, adopted by bad hackers. They want your money, and they know the best way to get it is to take away or “temporarily block” your email system until you pay to unblock it.
There are hundreds of successful criminal hackers using this business model to corrupt and steal cloud-based emails. We’re all at risk– This form of ransomware has worked its way into our inboxes.
How Does Ransomware in Real Time Work?
Let’s get back to the basics of what ransomware is and how it works. Ransomware is a type of malware. Its sole purpose is to block users from their data until a ransom is paid.
Ransomware is effective because of it’s difficult to unblock data without paying the ransom. The only other option, besides paying, is restoring a recent backup. This usually isn’t an option for most because of how often backups fail.
Hackers locate a target, (typically multiple ones) and bypass verification of both Google and Microsoft 365 email applications. They then tempt users with “anti-spam” service emails. It works with any cloud-based email service that uses OAuth to grant an application access to information without requiring passwords.
Employees are likely to click accept these emails because they trust their email systems to filter out messages that could potentially harm their accounts.
So now that your employee has accepted this phishing message, and all of their emails are encrypted, what do you do? The hackers will offer to “decrypt” the user’s emails at a price around $300-$400. If everyone in the company accepts the message, you’re looking at a major financial loss.
The best thing to do is to be prepared. Take the initiative and equip your employees with the knowledge and readiness to recognize and avoid phishing messages. Do this before it’s too late.
How to Avoid a Hack
To protect your company and documents, you must determine which employees are likely to accept phishing emails. Then you should train them to recognize this threat.
You must stay one step ahead of the bad guys. Preparing and training your team is the only way to fully avoid potential security attacks.
Like we mentioned before, this ransomware strain is in its early stages. But with criminal hackers successfully scoring major money from attacking big businesses, as well as everyday users, other hackers and cyber gangs are quickly taking notice. The effectiveness of ransomware is only encouraging more hackers to create and use this strain.
Ransomware isn’t going anywhere anytime soon. It’s only growing stronger. The best thing you can do for your company is to be prepared and not fall victim to these attacks.
by Felicien | Jan 19, 2018 | Education
First impressions are important. This is even more so in the world of technology. When searching for a company online, your first results appear in a small 160-character snippet. Now Google has officially extended the search results snippets to a maximum character length of 320 characters.
What is a snippet?
Snippets, also known as meta descriptions, refer to the HTML attribute that explains the contents of a given webpage. It’s a small description you see under the link on the search results page. Not only is this your first chance to snag your audience, but you are also being presented alongside other websites, and possibly competitors. This means you need to create and polish your snippet to ensure you make the best first impression possible.
How long should snippets be?
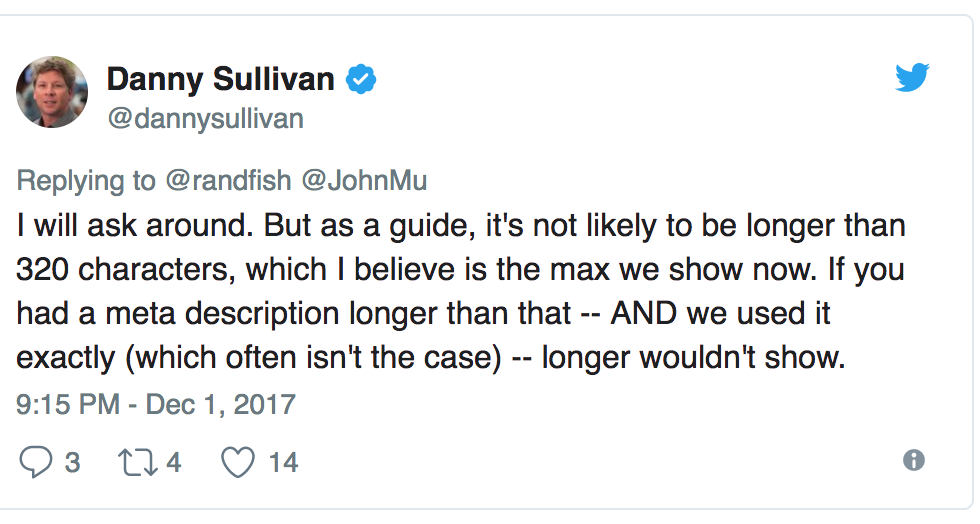
Danny Sullivan from Google explains in a tweet:
So, while your meta description is important, it doesn’t mean that Google will use it. Google is telling webmasters not to change their meta descriptions. Danny Sullivan from Google wrote,
“don’t go expanding your meta description tags.” He said the longer snippets are “more a dynamic process” Google automatically makes decisions based on the content on your page and the query.
Another Google spokesperson explains:
“We recently made a change to provide more descriptive and useful snippets to help people better understand how pages are relevant to their searches. This resulted in snippets becoming slightly longer, on average.”
What’s the average character and word length for various websites?
A survey of Canadian media consumption by Microsoft concluded that “the average attention span had fallen to eight seconds, down from 12 in the year 2000.” It appears that we now have a shorter attention span than goldfish. Another study, done by Hubspot, found that “headlines between 8–12 words in length got the most Twitter shares on average, while headlines with either 12 or 14 words got the most Facebook Likes.” What does this mean for our snippets? If you only have 8 seconds to impress a reader, what should you 320-character snippet say?
The benefits of the newly extended snippet according to Google:
It will help people instantly find out more about your products and services: Structured snippets give visitors a preview of the nature and range of your products and services before they click on your ad.
It will improve your return on investment: The additional information that appears with your ads can increase your ads’ relevance and click-through rates. This may help you improve your return on investment by attracting clicks from visitors who are more likely to be interested in what you have to offer.
Customizability: You can add structured snippets to the account, campaign, or ad group levels. Specify the dates, days of the week, or times of day your structured snippets are eligible to show.
What information does Google use to make snippets?
Google wants to provide each searcher a tailored list of results. This means that if the website’s meta description is well written, includes important keyword terms or phrases, and falls into the snippets new length of 320 characters, then Google could use that website’s meta description as the snippet. However, this is not always the case. In other situations, Google will sometimes pull content from the web page to display for the searcher.
Stephan Spencer writes in the article “Anatomy of a Google Snippet that “rather than leaving your snippet to chance, try to ‘convince’ the Google algorithm to use your meta description instead (assuming it’s well-written and compels the click-through, of course!) by incorporating the popular search terms in the meta description.”
How can you make the most of your first impression with snippets?
Previously, Google would cut off most meta descriptions or snippets after roughly two lines of text. Now, while the character count might be 320 characters you should keep it under that limit. This is important because snippets are similar to title tags and may be based on pixel count and cut off. Due to this, you might lose some of your characters. When each character counts towards a first impression, you want to ensure that none are cut off.
What Google does recommend is that you keep these best practices in mind when creating or optimizing structured snippets:
Provide enough information. Aim to include at least four values per header. Optimize for mobile users. Create shorter snippets to appeal to customers on-the-go.
Increase your options. Add more than one header-value set. Having multiple sets of structured snippets provides more options and increases the likelihood that a relevant extension will show with your ad.
Pick the right format. Unlike callout extensions, which can highlight a single unique aspect of your business in a few words, structured snippets should provide a complete group of products or services that your business provides.
Will Google do the same for Meta Descriptions?
While Google hasn’t officially provided a statement about making similar changes to meta descriptions, Danny Sullivan did reference a previous tweet from Google’s John Mueller. He states: “We’re always working on search, there’s not really anything specific to say there. I don’t think we ever had a limit on description meta tag content length.”





